


| The World Factbook | ||


|
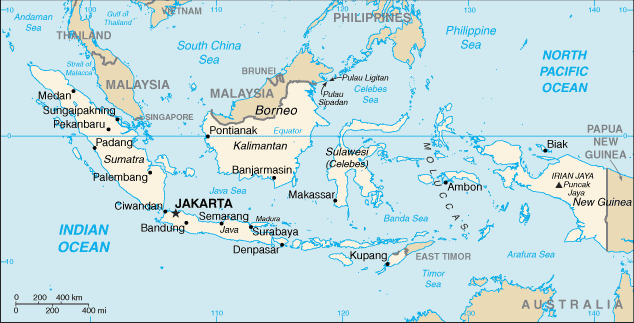
Indonesia |

|
|
| Introduction | Indonesia |
|
Background:
|
The Dutch began to colonize Indonesia in the early 17th century; the islands were occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1945. Indonesia declared its independence after Japan's surrender, but it required four years of intermittent negotiations, recurring hostilities, and UN mediation before the Netherlands agreed to relinquish its colony. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and home to the world's largest Muslim population. Current issues include: alleviating poverty, preventing terrorism, consolidating democracy after four decades of authoritarianism, implementing financial sector reforms, stemming corruption, and holding the military and police accountable for human rights violations. Indonesia was the nation worst hit by the December 2004 tsunami, which particularly affected Aceh province causing over 100,000 deaths and over $4 billion in damage. An additional earthquake in March 2005 created heavy destruction on the island of Nias. Reconstruction in these areas may take up to a decade. In 2005, Indonesia reached a historic peace agreement with armed separatists in Aceh, but it continues to face a low intensity separatist guerilla movement in Papua. |
| Geography | Indonesia |
|
Location:
|
Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
5 00 S, 120 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Southeast Asia |
|
Area:
|
total: 1,919,440 sq km
land: 1,826,440 sq km water: 93,000 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly less than three times the size of Texas |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 2,830 km
border countries: East Timor 228 km, Malaysia 1,782 km, Papua New Guinea 820 km |
|
Coastline:
|
54,716 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
measured from claimed archipelagic straight baselines
territorial sea: 12 nm exclusive economic zone: 200 nm |
|
Climate:
|
tropical; hot, humid; more moderate in highlands |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly coastal lowlands; larger islands have interior mountains |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
highest point: Puncak Jaya 5,030 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
petroleum, tin, natural gas, nickel, timber, bauxite, copper, fertile soils, coal, gold, silver |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 11.03%
permanent crops: 7.04% other: 81.93% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
45,000 sq km (2003) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
occasional floods, severe droughts, tsunamis, earthquakes, volcanoes, forest fires |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
deforestation; water pollution from industrial wastes, sewage; air pollution in urban areas; smoke and haze from forest fires |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation |
|
Geography - note:
|
archipelago of 17,508 islands (6,000 inhabited); straddles equator; strategic location astride or along major sea lanes from Indian Ocean to Pacific Ocean |
| People | Indonesia |
|
Population:
|
245,452,739 (July 2006 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 28.8% (male 35,995,919/female 34,749,582)
15-64 years: 65.8% (male 80,796,794/female 80,754,238) 65 years and over: 5.4% (male 5,737,473/female 7,418,733) (2006 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 26.8 years
male: 26.4 years female: 27.3 years (2006 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
1.41% (2006 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
20.34 births/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
6.25 deaths/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2006 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.77 male(s)/female total population: 1 male(s)/female (2006 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 34.39 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 39.36 deaths/1,000 live births female: 29.17 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 69.87 years
male: 67.42 years female: 72.45 years (2006 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
2.4 children born/woman (2006 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
0.1% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
110,000 (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
2,400 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever vectorborne diseases: dengue fever, malaria, and chikungunya are high risks in some locations note: at present, H5N1 avian influenza poses a minimal risk; during outbreaks among birds, rare cases could occur among US citizens who have close contact with infected birds or poultry (2005) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Indonesian(s)
adjective: Indonesian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Javanese 45%, Sundanese 14%, Madurese 7.5%, coastal Malays 7.5%, other 26% |
|
Religions:
|
Muslim 88%, Protestant 5%, Roman Catholic 3%, Hindu 2%, Buddhist 1%, other 1% (1998) |
|
Languages:
|
Bahasa Indonesia (official, modified form of Malay), English, Dutch, local dialects, the most widely spoken of which is Javanese |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 87.9% male: 92.5% female: 83.4% (2002 est.) |
| Government | Indonesia |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Indonesia
conventional short form: Indonesia local long form: Republik Indonesia local short form: Indonesia former: Netherlands East Indies; Dutch East Indies |
|
Government type:
|
republic |
|
Capital:
|
name: Jakarta
geographic coordinates: 6 10 S, 106 48 E time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) note: Indonesia is divided into three time zones |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
30 provinces (propinsi-propinsi, singular - propinsi), 2 special regions* (daerah-daerah istimewa, singular - daerah istimewa), and 1 special capital city district** (daerah khusus ibukota); Aceh*, Bali, Banten, Bengkulu, Gorontalo, Irian Jaya Barat, Jakarta Raya**, Jambi, Jawa Barat, Jawa Tengah, Jawa Timur, Kalimantan Barat, Kalimantan Selatan, Kalimantan Tengah, Kalimantan Timur, Kepulauan Bangka Belitung, Kepulauan Riau, Lampung, Maluku, Maluku Utara, Nusa Tenggara Barat, Nusa Tenggara Timur, Papua, Riau, Sulawesi Barat, Sulawesi Selatan, Sulawesi Tengah, Sulawesi Tenggara, Sulawesi Utara, Sumatera Barat, Sumatera Selatan, Sumatera Utara, Yogyakarta*
note: following the implementation of decentralization beginning on 1 January 2001, the 440 districts or regencies have become the key administrative units responsible for providing most government services |
|
Independence:
|
17 August 1945 (independence proclaimed); 27 December 1949 (Netherlands recognizes Indonesian independence) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day, 17 August (1945) |
|
Constitution:
|
August 1945; abrogated by Federal Constitution of 1949 and Provisional Constitution of 1950, restored 5 July 1959; series of amemdments concluded in 2002 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on Roman-Dutch law, substantially modified by indigenous concepts and by new criminal procedures and election codes; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
17 years of age; universal and married persons regardless of age |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Susilo Bambang YUDHOYONO (since 20 October 2004) and Vice President Muhammad Yusuf KALLA (since 20 October 2004); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Susilo Bambang YUDHOYONO (since 20 October 2004) and Vice President Muhammad Yusuf KALLA (since 20 October 2004); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections: president and vice president were elected for five-year terms (eligible for a second term) by direct vote of the citizenry; last held 20 September 2004 (next to be held in 2009) election results: Susilo Bambang YUDHOYONO elected president receiving 60.6% of vote; MEGAWATI Sukarnoputri received 39.4% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
House of Representatives or Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat (DPR) (550 seats; members elected to serve five-year terms); House of Regional Representatives (Dewan Perwakilan Daerah or DPD), constitutionally mandated role includes providing legislative input to DPR on issues affecting regions; People's Consultative Assembly (Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat or MPR) has role in inaugurating and impeaching president and in amending constitution; consists of popularly-elected members in DPR and DPD; MPR does not formulate national policy
elections: last held 5 April 2004 (next to be held in 2009) election results: percent of vote by party - Golkar 21.6%, PDI-P 18.5%, PKB 10.6%, PPP 8.2%, PD 7.5%, PKS 7.3%, PAN 6.4%, others 19.9%; seats by party - Golkar 128, PDI-P 109, PPP 58, PD 55, PAN 53, PKB 52, PKS 45, others 50 note: because of election rules, the number of seats won does not always follow the percentage of votes received by parties |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court or Mahkamah Agung (justices appointed by the president from a list of candidates approved by the legislature); a separate Constitutional Court or Mahkamah Konstitusi was invested by the president on 16 August 2003; in March 2004 the Supreme Court assumed administrative and financial responsibility for the lower court system from the Ministry of Justice and Human Rights; Labor Court under supervision of Supreme Court began functioning in January 2006 |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Crescent Moon and Star Party or PBB [MS KABAN]; Democratic Party or PD [Hadi UTOMO]; Functional Groups Party or Golkar [Yusuf KALLA]; Indonesia Democratic Party-Struggle or PDI-P [MEGAWATI Sukarnoputri]; National Awakening Party or PKB [MUHAIMIN Iskander]; National Mandate Party or PAN [Sutrisno BACHIR]; Prosperous Justice Party or PKS [Tifatul SEMBIRING]; United Development Party or PPP [Hamzah HAZ] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
NA |
|
International organization participation:
|
APEC, APT, ARF, AsDB, ASEAN, BIS, CP, EAS, FAO, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, MONUC, NAM, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PIF (partner), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNOMIG, UNWTO, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador SUDJADNAN Parnohadiningrat
chancery: 2020 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036 telephone: [1] (202) 775-5200 FAX: [1] (202) 775-5365 consulate(s) general: Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador B. Lynn PASCOE
embassy: Jalan 1 Medan Merdeka Selatan 4-5, Jakarta 10110 mailing address: Unit 8129, Box 1, FPO AP 96520 telephone: [62] (21) 3435-9000 FAX: [62] (21) 3435-9922 consulate(s) general: Surabaya consulate(s): Medan; Denpasar (consular agency) |
|
Flag description:
|
two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and white; similar to the flag of Monaco, which is shorter; also similar to the flag of Poland, which is white (top) and red |
| Economy | Indonesia |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Indonesia, a vast polyglot nation, has struggled to overcome the Asian financial crisis, and still grapples with high poverty and unemployment, inadequate infrastructure, endemic corruption, a fragile banking sector, a poor investment climate, and unequal resource distribution among regions. The country continues the slow work of rebuilding from the devastating December 2004 tsunami and from an earthquake in central Java in May 2006 that caused over $3 billion in damage and losses. Declining oil production and lack of new exploration investment turned Indonesia into a net oil importer in 2004. The cost of subsidizing domestic fuel placed increasing strain on the budget in 2005, and combined with indecisive monetary policy, contributed to a run on the currency in August, prompting the government to enact a 126% average fuel price hike in October. The resulting inflation and interest rate hikes dampened growth through mid-2006, while large increases in rice prices pushed millions more people under the national poverty line. Economic reformers introduced three policy packages in 2006 to improve the investment climate, infrastructure, and the financial sector, but translating them into reality has not been easy. Keys to future growth remain internal reform, building up the confidence of international and domestic investors, and strong global economic growth. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$935 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$264.4 billion (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
5.4% (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$3,800 (2006 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 13.1%
industry: 46% services: 41% (2006 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
108.2 million (2006 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 43.3%
industry: 18% services: 38.7% (2004 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
12.5% (2006 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
17.8% (2006) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 3.6%
highest 10%: 28.5% (2002) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
34.8 (2004) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
13.2% (2006 est.) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
20.3% of GDP (2006 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $75.58 billion
expenditures: $79.45 billion; including capital expenditures of $NA (2006 est.) |
|
Public debt:
|
43.8% of GDP (2006 est.) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
rice, cassava (tapioca), peanuts, rubber, cocoa, coffee, palm oil, copra; poultry, beef, pork, eggs |
|
Industries:
|
petroleum and natural gas, textiles, apparel, footwear, mining, cement, chemical fertilizers, plywood, rubber, food, tourism |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
2.6% (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
112.6 billion kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 86.9%
hydro: 10.5% nuclear: 0% other: 2.6% (2001) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
104.7 billion kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2004) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2004) |
|
Oil - production:
|
1.061 million bbl/day (2005 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
1.084 million bbl/day (2005 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
431,500 bbl/day (2004 est.) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
345,700 bbl/day (2005 est.) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
4.85 billion bbl (2006 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
83.4 billion cu m (2005 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
22.5 billion cu m (2005 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
37.5 billion cu m (2005 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2005 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
2.557 trillion cu m (1 January 2005 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$1.636 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$102.3 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
oil and gas, electrical appliances, plywood, textiles, rubber |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Japan 21.1%, US 11.5%, Singapore 9.2%, South Korea 8.3%, China 7.8%, Malaysia 4% (2005) |
|
Imports:
|
$77.73 billion f.o.b. (2006 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery and equipment, chemicals, fuels, foodstuffs |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Singapore 16.4%, Japan 12%, China 10.1%, US 6.7%, Thailand 6%, South Korea 5%, Saudi Arabia 4.7%, Australia 4.4% (2005) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$43.04 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$130.4 billion (2006 est.) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$43 billion (2002 est.)
note: Indonesia finished its IMF program in December 2003 but still receives bilateral aid through the Consultative Group on Indonesia (CGI), which pledged $2.8 billion in grants and loans for 2004 and again in 2005; nearly $5 billion in aid money pledged by a variety bilateral, multilateral, and non-governmental organization (NGO) donors following the 2004 tsunami; money is slated for use in relief and rebuilding efforts in Aceh |
|
Currency (code):
|
Indonesian rupiah (IDR) |
|
Currency code:
|
IDR |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Indonesian rupiah per US dollar - 9,207.18 (2006), 9,704.7 (2005), 8,938.9 (2004), 8,577.1 (2003), 9,311.2 (2002) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
calendar year; note - previously was 1 April - 31 March, but starting with 2001, has been changed to calendar year |
| Communications | Indonesia |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
12.772 million (2005) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
46.91 million (2005) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: domestic service fair, international service good
domestic: interisland microwave system and HF radio police net; domestic satellite communications system international: country code - 62; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (1 Indian Ocean and 1 Pacific Ocean) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 678, FM 43, shortwave 82 (1998) |
|
Radios:
|
31.5 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
54 local TV stations
note: 11 national TV networks; each with their own group of local, often low power, transmitters (2006) |
|
Televisions:
|
13.75 million (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.id |
|
Internet hosts:
|
170,834 (2006) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
24 (2000) |
|
Internet users:
|
16 million (2005) |
| Transportation | Indonesia |
|
Airports:
|
662 (2006) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 159
over 3,047 m: 4 2,438 to 3,047 m: 15 1,524 to 2,437 m: 49 914 to 1,523 m: 49 under 914 m: 42 (2006) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 503
1,524 to 2,437 m: 6 914 to 1,523 m: 26 under 914 m: 471 (2006) |
|
Heliports:
|
23 (2006) |
|
Pipelines:
|
condensate 944 km; condensate/gas 135 km; gas 9,175 km; oil 7,684 km; oil/gas/water 89 km; refined products 1,367 km (2006) |
|
Railways:
|
total: 6,458 km
narrow gauge: 5,961 km 1.067-m gauge (125 km electrified); 497 km 0.750-m gauge (2005) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 368,360 km
paved: 213,649 km unpaved: 154,711 km (2002) |
|
Waterways:
|
21,579 km (2005) |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 824 ships (1000 GRT or over) 3,773,771 GRT/4,887,614 DWT
by type: bulk carrier 43, cargo 451, chemical tanker 21, container 50, liquefied gas 7, livestock carrier 1, passenger 41, passenger/cargo 58, petroleum tanker 132, refrigerated cargo 2, roll on/roll off 12, specialized tanker 4, vehicle carrier 2 foreign-owned: 30 (France 1, Germany 1, Japan 3, South Korea 1, Norway 1, Philippines 1, Singapore 17, Switzerland 3, UK 2) registered in other countries: 122 (Bahamas 4, Belize 2, Bermuda 1, Cambodia 1, Georgia 1, Hong Kong 4, Liberia 1, Panama 50, Singapore 56, Thailand 1, unknown 1) (2006) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Banjarmasin, Belawan, Ciwandan, Krueg Geukueh, Palembang, Panjang, Sungai Pakning, Tanjung Perak, Tanjung Priok |
| Military | Indonesia |
|
Military branches:
|
Indonesia Armed Forces (Tentara Nasional Indonesia, TNI): Army (TNI-AD), Navy (TNI-AL, includes marines, naval air arm), Air Force (TNI-AU)
note: the TNI is directly subordinate to the president but the government is making efforts to incorporate it into the Department of Defense |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; conscript service obligation - two years (2002) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 60,543,028
females age 18-49: 59,981,730 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 18-49: 48,687,234
females age 18-49: 50,252,911 (2005 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching military service age annually:
|
males age 18-49: 2,201,047
females age 18-49: 2,139,573 (2005 est.) |
|
Military expenditures - dollar figure:
|
$1.3 billion (2004) |
|
Military expenditures - percent of GDP:
|
3% (2004) |
| Transnational Issues | Indonesia |
|
Disputes - international:
|
East Timor-Indonesia Boundary Committee continues to meet, survey, and delimit land boundary, but several sections of the boundary remain unresolved; many East Timorese refugees who left in 2003 still reside in Indonesia and refuse repatriation; Indonesia and East Timor contest the sovereignty of the uninhabited coral island of Pulau Batek/Fatu Sinai, which hinders a decision on a northern maritime boundary; a 1997 treaty between Indonesia and Australia settled some parts of their maritime boundary but outstanding issues remain; ICJ's award of Sipadan and Ligitan islands to Malaysia in 2002 left maritime boundary in the hydrocarbon-rich Celebes Sea in dispute, culminating in hostile confrontations in March 2005 over concessions to the Ambalat oil block; the ICJ decision has prompted Indonesia to assert claims to and to establish a presence on its smaller outer islands; Indonesia and Singapore pledged in 2005 to finalize their 1973 maritime boundary agreement by defining unresolved areas north of Batam Island; Indonesian secessionists, squatters, and illegal migrants create repatriation problems for Papua New Guinea; piracy remains a problem in the Malacca Strait |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
IDPs: 570,000 (resulting from 26 December 2004 tsunami) 500,000 (government offensives against rebels in Aceh; most IDPs in Aceh, Central Kalimantan, Maluku, and Central Sulawesi Provinces); (2005) |
|
Trafficking in persons:
|
current situation: Indonesia is a source, transit, and destination country for women, children and men trafficked for the purposes of sexual exploitation and forced labor; Indonesian victims are trafficked to Malaysia, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore; a significant number of Indonesian women who go overseas each year to work as domestic servants or "cultural performers" are subjected to conditions of involuntary servitude and commercial sexual exploitation; to a minimal extent, Indonesia is a destination for women from East Asia, Europe, and South America who are trafficked for sexual exploitation; there is extensive trafficking within Indonesia from rural to urban metropolitan areas particularly for sexual exploitation and involuntary domestic servitude
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Indonesia is placed on the Tier 2 Watch List for its failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to combat trafficking |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
illicit producer of cannabis largely for domestic use; producer of methamphetamine and ecstasy |
|
This page was last updated on 18 January, 2007 |