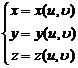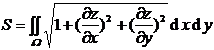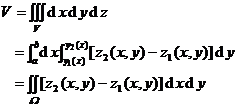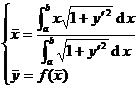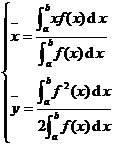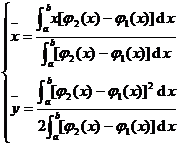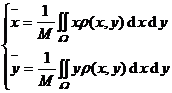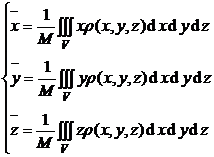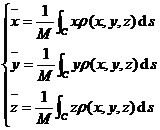§ 3 Application of credits
1. Find the area
[ Calculation formula for the area of plane graphics ]
|
graphics |
Area S |
|
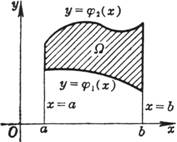
Curved trapezoid |
|
|
|
|
|
graphics |
Area S |
|
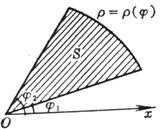
sector
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S = or S =2 where s represents the curve equation on , s represents the length of the curve on , d s is the differential of the arc, and is the center of gravity of the curve The distance from G to the axis of rotation . |
|
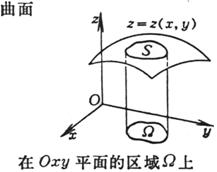
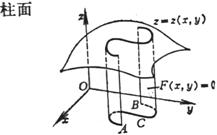
surface on the area |
in the formula
|
|
Cylinder sandwiched between surface and plane |
where C is the directrix of the cylinder, d s is the arc on the curve C ( A, B ) points . |
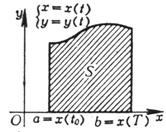
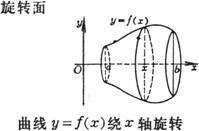
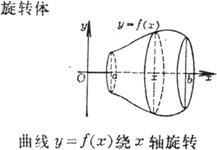
2. Find the volume
|
graphics |
Volume V |
|
|
where is the curve equation above |
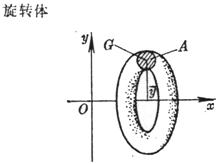
|
|
In the formula, A is the area of the plane figure to be rotated , and it is the distance from the center of gravity G of the plane figure to the rotation axis ( x -axis) . |
|
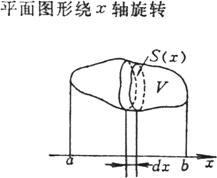
|
where S ( x ) is the cross-sectional area perpendicular to the x -axis |
|
on surfaces and regions |
|
|
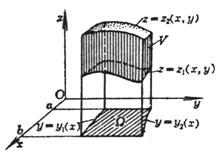
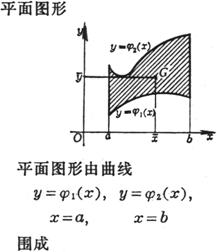
The spatial region V is bounded by the following surfaces:
|
where is the area on the Oxy plane, which is surrounded by curves , |
3. The formula for the volume of a convex body in n - dimensional space
The coordinates of a point in the n -dimensional space are ( ![]() ). The so-called convex body in the n -dimensional space means that the line connecting any two points A and B in the n-dimensional space is still in the middle, that is, let A = B = , if A , B ∈ , then point . of which
). The so-called convex body in the n -dimensional space means that the line connecting any two points A and B in the n-dimensional space is still in the middle, that is, let A = B = , if A , B ∈ , then point . of which![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , i =1,2, … , n
, i =1,2, … , n
The following are some formulas for calculating the volume of a convex body .
[ Simplex ] Known n + 1 points in n -dimensional space, the smallest convex body containing these n + 1 points is called a simplex formed by Zhang, denoted as , if the n coordinates are set as![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
( ) i =1 ,2 , ![]() … , n +1
… , n +1
then the volume of the simplex![]()
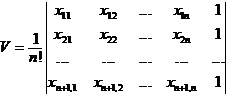
When n = 2 it is a triangle, when n = 3 it is a tetrahedron .
[ Hypercube ]
![]() : |
: | ![]() | ≤ , i =1,2, … , n
| ≤ , i =1,2, … , n![]()
V =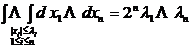
[ Generalized Octahedron ]
1 ° 1 : ≤ r , >0, i =1 ,2 , … , n![]()
![]()
![]()
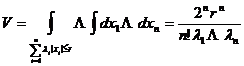
2 ° 2 : ≤ r , >0, >0 , i =1 ,2 , … , n- 1![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
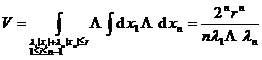
[ n -dimensional sphere ]
![]() :
:![]()
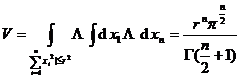
[ Linear transformation of convex body ] with linear transformation
![]() = , i =1,2,
= , i =1,2,![]() … , n
… , n
J = det( d ij ) ≠ 0
If the convex body R is mapped into , then the volume is![]()
![]()
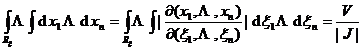
Here is the Jacobian of this linear transformation .![]()
![]()
Fourth, seek the center of gravity
[ Calculation formula of geometric barycentric coordinates of plane graphics ]
|
graphics |
geometric center of gravity |
|
flat curve
|
|
|
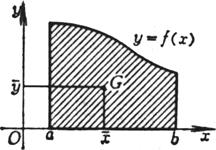
Curved trapezoid
|
|
|
|
|
[ Calculation formula of the total mass of the object and the coordinates of the center of gravity ]
|
Object shape and density |
Total mass M and center of gravity |
|
sheet
|
|
|
Object shape and density |
Total mass M and center of gravity |
|
|
|
|
|
In the formula, d s is the differential of the arc, and the above integral is the curve integral. |
Fifth, find the moment of inertia
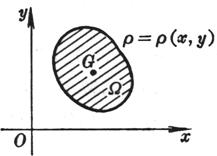
[ Moment of inertia of thin plate ] Let the density of thin plate Ω in the Oxy plane be ρ = ρ ( x,y ) , for the x - axis and y -axis, the moment of inertia of the origin O is respectively , then![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
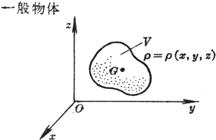
[ Moment of inertia of a general object ] Let the density ρ of the object V = ρ ( x, y, z ). If the moment of inertia of the object to the coordinate plane is respectively ; the moment of inertia of the object to a certain axis l is ; the rotation of the object to the coordinate axis Inertia respectively ; the moment of inertia of the object about the origin is , then![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
where r is the distance from the moving point of the object to the axis l .
![]()
![]()
![]()
|
|
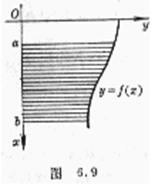
6. Find the fluid pressure
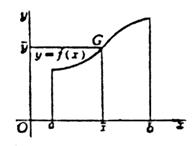
Assuming that the edge curve of the fluid contact surface is y=f(x) (Figure 6.9), and the fluid density is w , then the unilateral pressure
![]()
Seven, the work done by the change force
1 ° If s is the distance and f ( s ) is the variable force, then
![]()
2 °If s is the distance, the motion route is C , f ( x , y ) is the variable force, and θ is the angle between the variable force f and the tangent of the route C , then
![]()
3 °If the three components of the variable force along the coordinate axis are P ( x,y,z ), Q ( x,y,z ), R ( x,y,z ) , and C is the space motion route, then
![]()