§ 2 Generalized Fourier series and Fourier - Bessel series
1. Generalized Fourier Series
If the continuous function is
![]() ( 1 )
( 1 )
Orthogonal on a certain interval , and if the function is absolutely integrable on , then the![]()
![]()
![]()

is the series of coefficients
![]()
is called the generalized Fourier series of functions with respect to the orthogonal function system ( 1 ) , denoted as![]()
f ( x ) ~![]()
![]() are called the Fourier coefficients of the orthogonal function system ( 1 ) .
are called the Fourier coefficients of the orthogonal function system ( 1 ) .![]()
Let ( 1 ) be a standard orthogonal function system, that is, it satisfies
![]()
then
![]()
At this time, with respect to, there is Bessel's inequality![]()
![]() (
( ![]() is a square integrable function
is a square integrable function ![]()
If for any square-integrable function, the closedness equation
![]()
It is said that the orthogonal function system at this time is closed .![]()
2. Fourier - Bessel series
[ Fourier - Bessel series ]
1 Let o be the positive root of the Bessel function (see Chapter 12), then the function system![]()
![]()
![]()
Orthogonal by weight x on [0, 1] , i.e.
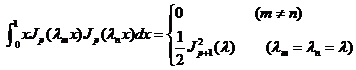
2 o For all functions that are absolutely integrable on [0, 1] , its Fourier - Bessel series can be made![]()
f ( x ) ~![]()
in the formula 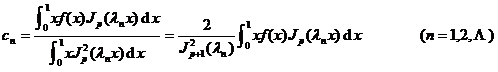
![]() are called the Fourier - Bessel coefficients of a function .
are called the Fourier - Bessel coefficients of a function .![]()
3 o If it is continuous everywhere on [0, 1] except for a finite number of discontinuous points of the first kind and is segment-wise differentiable, then its Fourier - Bessel series converges at that time, and at the continuous points, the series The sum equals , at the discontinuity, the series sum equals ;![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
If it is absolutely integrable on [0 , 1] , continuous in the interval and has absolutely integrable derivatives, then its Fourier-Bessel series converges uniformly in every interval ;![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
If it is absolutely integrable over [0 , 1] , continuous over the interval and has absolutely integrable derivatives, at the same time , then its Fourier - Bessel series converges uniformly over every interval .![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
[ Fourier - Bessel series of the second kind ]
1 o Let it be![]()
![]() ( H is a constant)
( H is a constant)
The positive root of , then, at that time , the function system![]()
![]()
Orthogonal by weight x on [0, 1] .
If it is absolutely integrable on [0 , 1] , then its generalized Fourier series with respect to the above orthogonal system is called a Fourier - Bessel series of the second kind , namely![]()
![]()
![]() ~
~![]()
in the formula 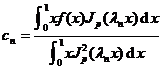
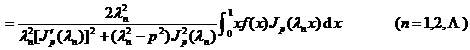
2 o If the function is piecewise differentiable on [0, 1] (with at most a finite number of discontinuities of the first kind), then its Fourier - Bessel series of the second kind converges on 0 < x < 1 , and Equal at continuous points and equal at discontinuous points ;![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
If the function is continuous on [0 , 1] , twice differentiable (except for a finite number of points), and = 0, , bounded, then its second kind of Fourier - Bessel series is then , at each The interval [ ,1] (0< <1) is absolutely and uniformly convergent; at the same time , it is absolutely and uniformly converged on the entire interval [0 , 1] .![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
[ Fourier - Bessel series over the interval [0 , l ] ]
Suppose it is absolutely integrable on [0 , l ] , then its Fourier - Bessel series is![]()
f ( x ) ~![]()
in the formula
![]()
![]()
For the Fourier - Bessel series of the second kind,
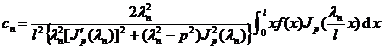
![]()
Regarding the convergence of the series, we can only discuss the convergence of the corresponding Fourier - Bessel series on [0 , 1] by transforming , .![]()
![]()
![]()