Chapter 2 Calculation and Drawing of Elementary Geometric Figures
Geometric figures are abstracted from the real world, so the theory, calculation and drawing of geometric figures are widely used in people's social practice .
This chapter focuses on two types of commonly used geometric figures: one is plane figures, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, regular polygons and various figures related to circles; the other is spatial three-dimensional figures, such as cubes, cuboids, spheres, cones, cylinders And various regular polyhedrons . The calculation formulas of their area, volume, side area, surface area, center of gravity and moment of inertia are collected in more detail here .
In addition, the drawing methods of some figures (such as regular polygons) are also introduced, and the ellipse drawing method and the arc lofting method commonly used in production practice are also briefly explained . The so-called "three major problems of geometry" that have been strictly proved cannot be drawn with rulers and compass .
§ 1 Triangles and quadrilaterals
First,
the calculation of the elements of the triangle
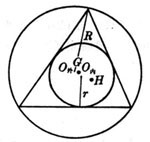
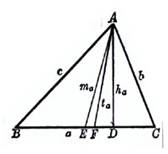
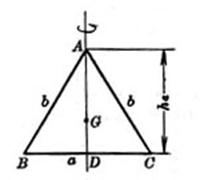
1. Elements of a triangle
Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2
a, b, c are the three sides of the triangle and R is the radius of the circumcircle
A , B, C are the three angles r is the radius of the inscribed circle![]()
AD is the height on the a side and H is the vertical center (the intersection of the three heights)![]()
AF is the bisector of angle A and G is the center of gravity (the intersection of the three medians)![]()
AE![]() is the center line on the side of a (the intersection of the three angle bisectors)
is the center line on the side of a (the intersection of the three angle bisectors)
![]()
![]() is the half perimeter as the circumcentre (the intersection of three perpendicular bisectors)
is the half perimeter as the circumcentre (the intersection of three perpendicular bisectors)![]()
![]()
S is the area of![]()
![]()
2. Calculation formula of each element of triangle
[ high ]
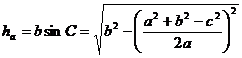
[ midline ] ![]()
[ angular bisector ]
![]()
[ area ]
![]()
[ Circumscribed circle radius ]
![]()
[ Inscribed circle radius ]
![]()
2.
Calculation formulas for the area, geometric center of gravity, and moment of inertia of triangles and quadrilaterals
|
graphics |
Area S , geometric center of gravity G and moment of inertia * J |
|
|
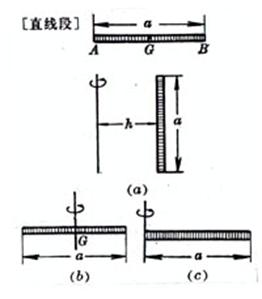
length L=a Center of gravity GA=GB = Moment of inertia (a) The axis of rotation is parallel to the thin rod, and the distance to the thin rod is h( figure ( a ))
(b) The rotating shaft passes through the center of gravity G of the thin rod ,and is connected to the thin rod vertical ( figure ( b ))
(c) The axis of rotation passes through one end of the thin rod,and is connected to Rod vertical ( figure ( c ))
|
![]() In the table, m is the mass of the object, and the objects are all homogeneous . For the calculation formula of the moment of inertia of general objects, see Chapter 6,
In the table, m is the mass of the object, and the objects are all homogeneous . For the calculation formula of the moment of inertia of general objects, see Chapter 6,
§ 3 , 5 .
|
graphics |
Area S , geometric center of gravity G and moment of inertia J |
|
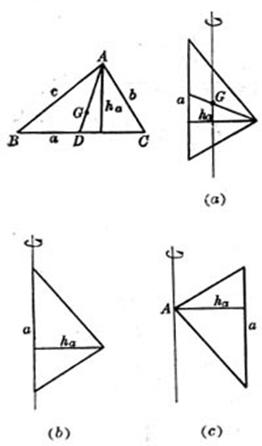
[ arbitrary triangle ]
a,b,c are three sides , [ isosceles triangle ]
b is the waist , a is the bottom edge , and |
center of gravity Moment of inertia ( a ) The axis of rotation passes through the center of gravity G and is parallel to side a ( Figure ( a )) ( b ) the axis of rotation coincides with the side a of the triangle ( figure ( b )) ( c ) the axis of rotation passes through a vertex A of the triangle and is parallel to side a ( figure ( c ))
center of gravity Moment of inertia The shaft coincides with the height on the bottom edge when a =b
|
|
graphics |
Area S , geometric center of gravity G and moment of inertia J |
|
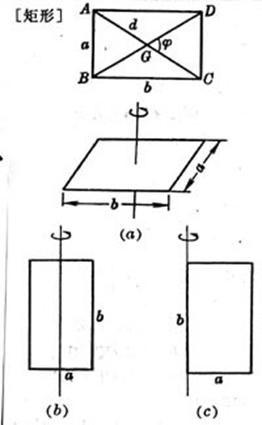
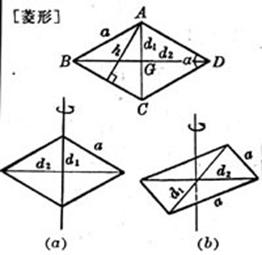
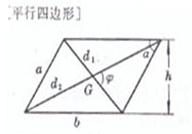
a, b are adjacent sides , d is the diagonal , and
a is the length of the side , |
area The center of gravity G is at the intersection of the diagonals , i.e. Moment of inertia ( a ) The axis of rotation passes through the center of the rectangle and is perpendicular to the plane where the rectangle is located ( Figure ( a )) ( b ) The axis of rotation passes through the center of the rectangle and is parallel to the b side of the rectangle ( Figure ( b )) ( c ) The axis of rotation coincides with the b side of the rectangle ( Figure ( c )) area The center of gravity G is at the intersection of the diagonals , i.e. Moment of inertia ( a ) The axis of rotation coincides with the diagonal ( Fig. ( a )) ( b ) The rotation axis passes through the center of gravity G and is perpendicular to the plane where the figure is located ( Figure ( b )) |
|
graphics |
Area S , geometric center of gravity G and moment of inertia J |
|
a, b are the adjacent sides , h is the distance between the opposite sides ,
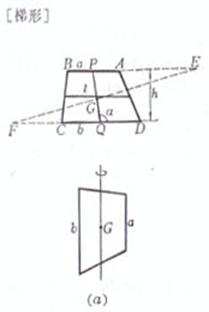
a, b are the upper and lower bases , h is the height , and l is the line connecting the midpoints of the two waists
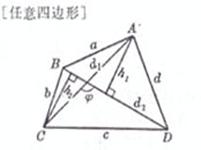
a, b, c, d are the lengths of the four sides , |
area The center of gravity G is at the intersection of the diagonals area center of gravity Moment of inertia The axis of rotation passes through the center of gravity and is parallel to the upper and lower bottoms ( Figure ( a )) When a =b ( parallelogram ) area
or |