|
|
|
The unique 2-Polyomino consisting of two equal squares connected along a complete Edge.
The Fibonacci Number ![]() gives the number of ways for
gives the number of ways for ![]() dominoes to cover a
dominoes to cover a ![]() Checkerboard, as illustrated in the following diagrams (Dickau).
Checkerboard, as illustrated in the following diagrams (Dickau).
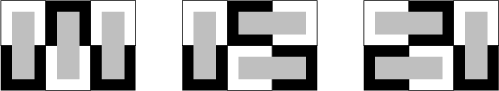
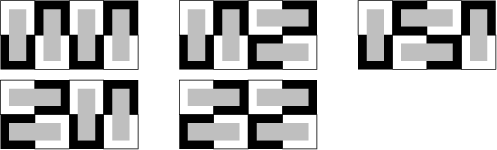
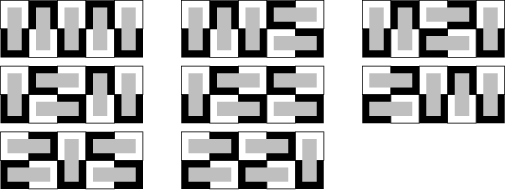
See also Fibonacci Number, Gomory's Theorem, Hexomino, Pentomino, Polyomino, Tetromino, Triomino
References
Dickau, R. M. ``Fibonacci Numbers.''
http://www.prairienet.org/~pops/fibboard.html.
Gardner, M. ``Polyominoes.'' Ch. 13 in The Scientific American Book of Mathematical Puzzles & Diversions.
New York: Simon and Schuster, pp. 124-140, 1959.
Kraitchik, M. ``Dominoes.'' §12.1.22 in Mathematical Recreations. New York: W. W. Norton,
pp. 298-302, 1942.
Lei, A. ``Domino.'' http://www.cs.ust.hk/~philipl/omino/domino.html.
Madachy, J. S. ``Domino Recreations.'' Madachy's Mathematical Recreations. New York: Dover, pp. 209-219, 1979.