|
|
|
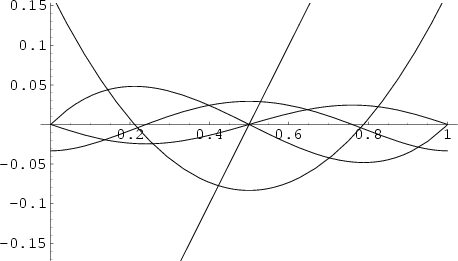
There are two definitions of Bernoulli polynomials in use. The ![]() th Bernoulli polynomial is denoted here by
th Bernoulli polynomial is denoted here by ![]() ,
and the archaic Bernoulli polynomial by
,
and the archaic Bernoulli polynomial by ![]() . These definitions correspond to the Bernoulli Numbers evaluated at 0,
. These definitions correspond to the Bernoulli Numbers evaluated at 0,
| (1) | |||
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
![\begin{displaymath}
\sum_{k=0}^{m-1} k^{n-1}={1\over n}[B_n(m)-B_n(0)].
\end{displaymath}](b_650.gif) |
(5) |
 |
(6) |
| (7) |
| (8) |
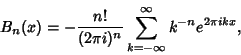 |
(9) |
 |
(10) |
A sum identity involving the Bernoulli Polynomials is
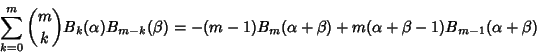 |
(11) |
See also Bernoulli Number, Euler-Maclaurin Integration Formulas, Euler Polynomial
References
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, C. A. (Eds.). ``Bernoulli and Euler Polynomials and the Euler-Maclaurin Formula.''
§23.1 in Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas,
Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, 9th printing. New York: Dover, pp. 804-806, 1972.
Appell, P. E. ``Sur une classe de polynomes.'' Annales d'École Normal Superieur, Ser. 2 9, 119-144,
1882.
Arfken, G. Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 3rd ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press, p. 330, 1985.
Bernoulli, J. Ars conjectandi. Basel, Switzerland, p. 97, 1713. Published posthumously.
Euler, L. ``Methodus generalis summandi progressiones.'' Comment. Acad. Sci. Petropol. 6, 68-97, 1738.
Lehmer, D. H. ``A New Approach to Bernoulli Polynomials.'' Amer. Math. Monthly. 95, 905-911, 1988.
Lucas, E. Ch. 14 in Théorie des Nombres. Paris, 1891.
Raabe, J. L. ``Zurückführung einiger Summen und bestimmten Integrale auf die Jakob Bernoullische Function.''
J. reine angew. Math. 42, 348-376, 1851.
Spanier, J. and Oldham, K. B. ``The Bernoulli Polynomial
![]() .''
Ch. 19 in An Atlas of Functions. Washington, DC: Hemisphere, pp. 167-173, 1987.
.''
Ch. 19 in An Atlas of Functions. Washington, DC: Hemisphere, pp. 167-173, 1987.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein