|
|
|
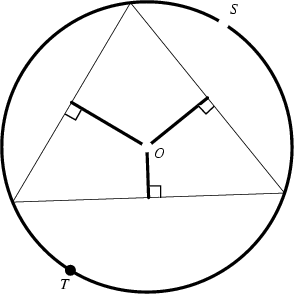
A Triangle's circumscribed circle. Its center ![]() is called the Circumcenter, and its Radius
is called the Circumcenter, and its Radius ![]() the
Circumradius. The circumcircle can be specified using Trilinear Coordinates as
the
Circumradius. The circumcircle can be specified using Trilinear Coordinates as
| (1) |
A Geometric Construction for the circumcircle is given by Pedoe (1995, pp. xii-xiii). The equation for the
circumcircle of the Triangle with Vertices ![]() for
for ![]() , 2, 3 is
, 2, 3 is
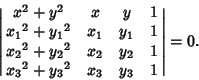 |
(2) |
| (3) |
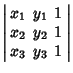 |
(4) | ||
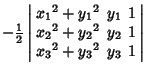 |
(5) | ||
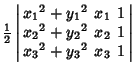 |
(6) | ||
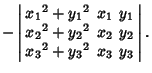 |
(7) |
| (8) |
| (9) |
| (10) | |||
| (11) |
| (12) |
See also Circle, Circumcenter, Circumradius, Excircle, Incircle, Parry Point, Purser's Theorem, Steiner Points, Tarry Point
References
Pedoe, D. Circles: A Mathematical View, rev. ed. Washington, DC: Math. Assoc. Amer., 1995.
|
|
|
© 1996-9 Eric W. Weisstein